MDF is a composite panel product consisting of cellulosic fibers combined with a synthetic resin or other bonding systems, joined together under heat and pressure. Additives may be introduced during manufacturing to convey certain characteristics, including additional moisture and fire resistance properties.
MDF panels are manufactured with a wide range of physical properties and dimensions for many end-product design specifications. The consistent density profile of MDF allows intricate and precise machining and finishing techniques, including routing, for the manufacture of superior products. Additionally, trim waste is significantly reduced when using MDF compared to other substrates. Stability and strength are important assets of MDF, which can be machined into complex patterns that require precise tolerances.

Inspirations: MDF can be machined into complex patterns with tight tolerances and is ideal for use in cabinetry, furniture, flooring, retail fixtures, millwork and trim, or other applications where edge shaping, embossing, laminating or finishing is required.
Its surface is flat, smooth, uniform, dense and free of knots and grain patterns. Its low surface variance makes it extraordinarily smooth and the ideal substrate for a wide variety of finishes including high gloss and paint. For these reasons and many others, MDF is widely used in the manufacture of furniture, kitchen cabinets, door parts, mouldings, millwork and laminate flooring.
|
MORE INFO Read the complete Design Portfolio: The definitive guide to sourcing decorative surfaces and composite panels.
Composite Panel Association
More information, plus industry news, testing & certification, policy and stewardship at the Composite Panel Association's website CompositePanel.org |

|
Product Standards, Certification, and Environmental Specifications
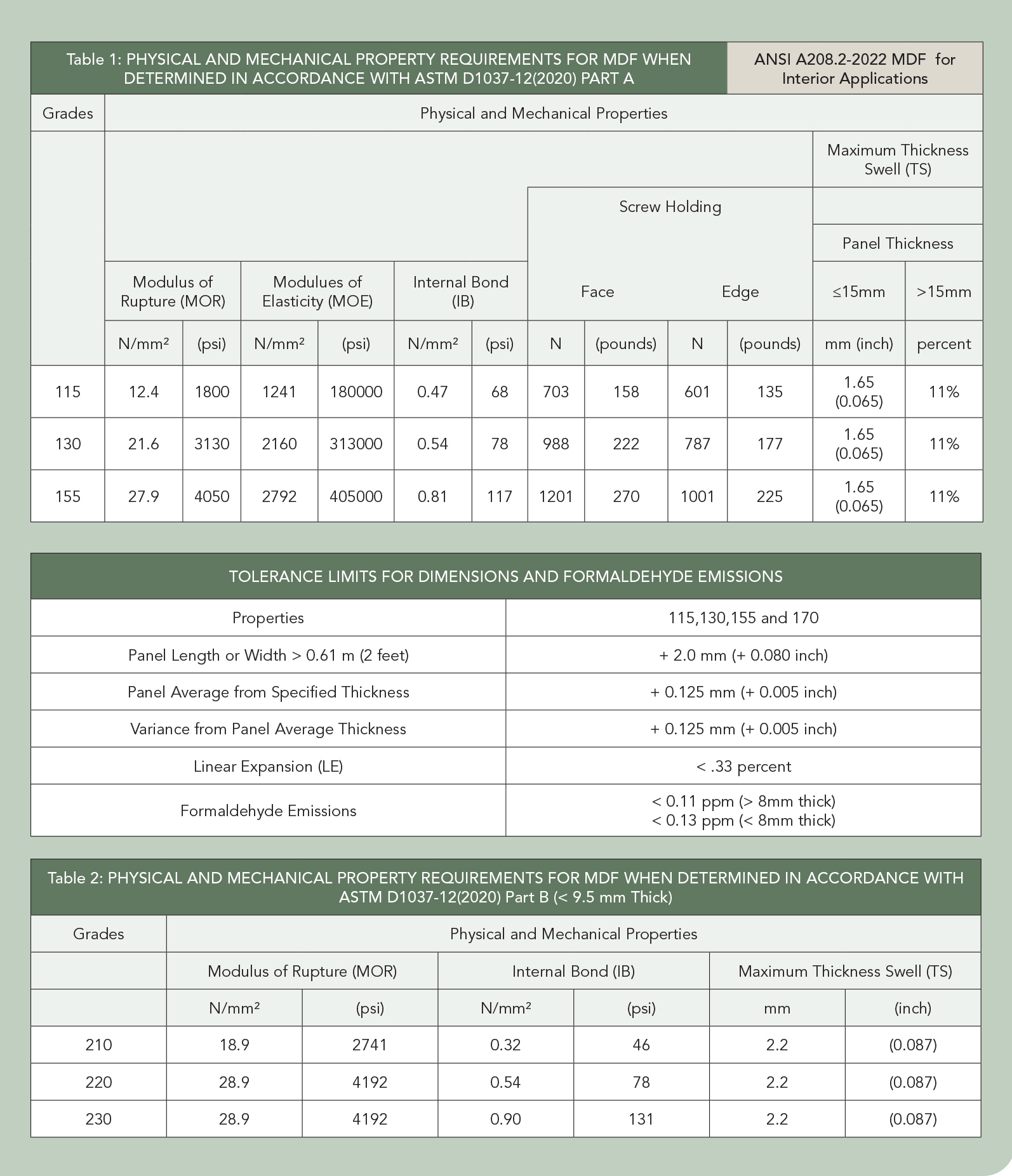
The ANSI A208.2 Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) for Interior Applications is the North American industry voluntary standard for use and specification. It classifies MDF by physical and mechanical properties and identifies product grades for MDF and thin MDF. Specifications identified in the standard include physical properties, dimensional tolerances, mechanical properties and formaldehyde emission limits. The standard is sponsored by the Composite Panel Association (CPA) and is developed in conjunction with industry stakeholders including producers, users and other interested groups. A summary of the MDF Property Requirements is shown below, and copies of ANSI A208.2 are available on the CPA website, CompositePanel.org.
Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) are the widely accepted standardized specification format for communicating a product’s environmental footprint and performance. EPDs are the definitive source of technical environmental data based on life cycle analysis (LCA) and can be used to compare alternative product materials directly. Read the article “Selecting Composite Wood Panels” in Design Portfolio for additional information.
Formaldehyde Emission Limits
All manufacturers of MDF panels sold in the U.S. and Canada must meet the third-party certification and formaldehyde emissions testing requirements, no added formaldehyde (NAF) or ultra-low emitting formaldehyde (ULEF) designation under the EPA TSCA Title VI and California Air Resources Board Airborne Toxic Control Measure (CARB ATCM 93120) regulations or the Canadian regulations (CANFER, DORS / 2021-148).
In compliance with EPA TSCA Title VI, third-party certified panels are allowed a maximum of 0.11 ppm for MDF panels thicker than 8mm, 0.13 ppm maximum limit for thin MDF (< 8mm), 0.04 ppm for NAF/ULEF exempt, 0.06 ppm (MDF) and 0.08 ppm (thin MDF) for ULEF-reduced testing. Those companies currently producing ULEF and NAF products are identified in the product listings in this issue of Design Portfolio.
In addition, CPA’s Eco-Certified Composite (ECC) Sustainability Standard Certification Program requires that certified participants meet the stringent emission limits in the EPA TSCA Title VI and CARB ATCM 93120 regulations for 100% of the facility’s manufactured panels.
Finally, various overlays and surface treatments have significantly reduced product emissions. For additional information about emissions, see the CPA Technical Bulletin “VOC Emission Barrier Effects.”
View a spec chart of Composite Panel Association members that produce MDF.






Have something to say? Share your thoughts with us in the comments below.